Understanding Actuator Valves How They Work and Their Applications
In the realm of industrial automation and control systems, actuator valves play a crucial role in regulating the flow of liquids and gases. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the actuator valve market is projected to reach USD 12.01 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.1% from 2020. This growth is largely driven by increasing demand for automation in various sectors including oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical manufacturing. Actuator valves are essential components that facilitate precise control, enhancing operational efficiency and safety in complex processes.
Expert opinions also highlight the significance of actuator valves in modern applications. Dr. Linda Thomason, an authority on automation technology, stated, "The integration of actuator valves into control systems enhances not only efficiency but also the reliability of critical processes." This underscores the necessity of understanding how actuator valves function. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable in both traditional industries and emerging technologies, proving their vital role in shaping the future of automation. As industries continue to evolve towards more integrated systems, a deeper comprehension of actuator valves will be fundamental for engineers and technicians alike.

Understanding Actuator Valves: Definition and Purpose
Actuator valves play a crucial role in various industrial processes by regulating the flow of fluids in systems. Defined as devices that control the opening and closing of valves based on input signals, actuator valves serve essential functions in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing. According to a market research report from Transparency Market Research, the global actuator market is expected to grow significantly, reaching approximately $34.6 billion by 2027. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on automation in industrial settings, as actuator valves enhance operational efficiency and safety.
Understanding the purpose of actuator valves is critical for engineers and operators in the field. These valves not only facilitate accurate flow control but also contribute to system integrity and performance optimization. By automating the valve operation, industries can achieve precise control over fluid dynamics, resulting in reduced energy consumption and minimized waste. This is particularly beneficial in sectors where minimizing environmental impact is a priority, as optimizing fluid flow can lead to more sustainable practices.
Tip: When selecting actuator valves for your application, consider factors such as material compatibility, actuator type (pneumatic vs. electric), and response time to ensure optimal performance tailored to your specific needs. Additionally, regular maintenance of these valves is essential to prolong their lifespan and maintain efficient operations.
Components of Actuator Valves: Key Parts Explained
Actuator valves are essential components in numerous industrial applications, offering precise control over fluid flow and pressure. Understanding the key parts that make up an actuator valve is crucial for maximizing efficiency and reliability. The primary components include the valve body, actuator mechanism, and various controls. The valve body is typically designed to withstand specific environmental conditions while facilitating the desired flow characteristics. It houses the internal mechanisms and features, such as seats and seals, which ensure a tight closure to prevent leakage.
The actuator mechanism is arguably the heart of the actuator valve. It converts energy, usually in the form of electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic signals, into mechanical motion to open or close the valve. This mechanism may include gears, levers, or linkages, which enhance the responsiveness and positioning accuracy of the valve. Additionally, control systems often integrate sensors and feedback loops, further improving operation by allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustments.
Another critical aspect of actuator valves is their various control options. Manual, automatic, and remotely operated controls provide flexibility in operation, meeting the needs of different applications. Moreover, safety features, such as fail-safe actuators and limit switches, are often included to ensure that the system can handle unexpected failures effectively. Understanding these components helps engineers design systems that are not only functional but also safe and efficient, addressing the demands of modern industrial processes.
How Actuator Valves Function: Mechanisms and Principles
Actuator valves are critical components in various industrial applications, utilizing specific mechanisms to regulate fluid flow. At their core, actuator valves operate through a combination of mechanical energy and control signals. They consist of two main parts: the valve itself and the actuator, which can be either manual, pneumatic, or electric. The actuator converts the control signal into mechanical motion, enabling the valve to open or close as needed. This transformation of energy allows for precise flow control, adapting to fluctuating system demands.
The functioning principle of actuator valves can be broadly categorized into two primary types: linear and rotary actuators. Linear actuators move the valve stem vertically, providing straightforward modulation for throttling applications. In contrast, rotary actuators rotate the valve disc or ball, facilitating rapid on-off control, essential in systems that require quick response times. Both mechanisms often incorporate feedback sensors, ensuring that the actuator accurately reflects the desired position of the valve. This closed-loop control enhances reliability and efficiency in various processes, from water treatment to chemical processing. Understanding these principles is crucial for optimizing the performance and longevity of systems utilizing actuator valves.
Applications of Actuator Valves: Industries and Use Cases
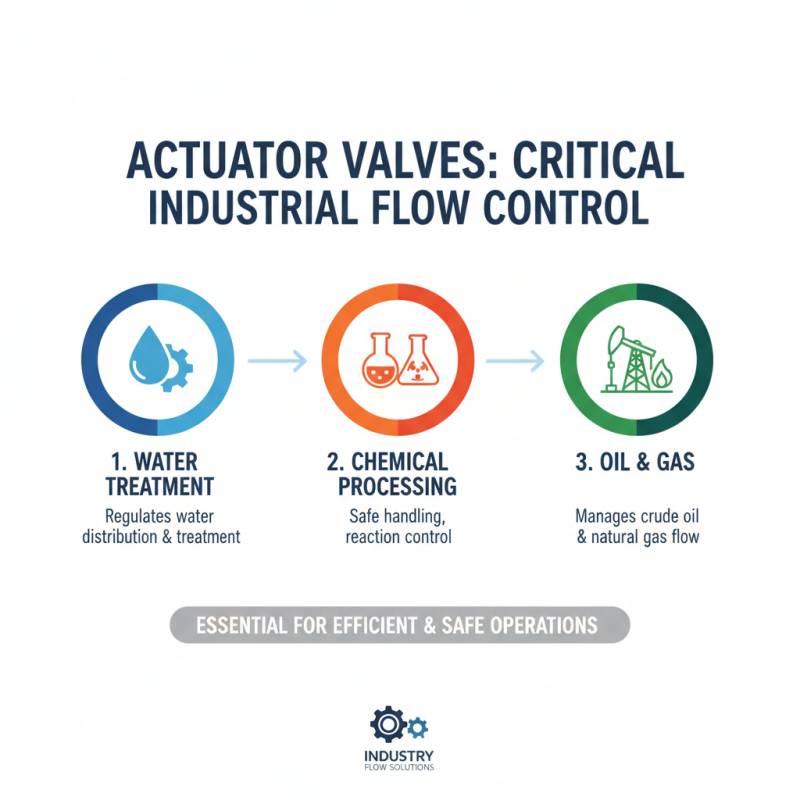
Actuator valves play a crucial role across various industries by controlling the flow of liquids and gases. These devices are often used in water treatment facilities to regulate the distribution of water and ensure proper treatment processes. In chemical processing plants, actuator valves are essential for maintaining the safe handling of hazardous materials, enabling precise control over reactions and mixtures. Additionally, in the oil and gas sector, actuator valves help manage the flow of crude oil and natural gas, contributing to efficient extraction and processing operations.
Tips: When selecting an actuator valve for a specific application, consider factors such as the type of media being controlled, the required pressure and temperature ratings, and the desired response time. Ensuring that the actuator valve is compatible with the system can greatly enhance performance and reduce maintenance costs.
In the pharmaceutical industry, actuator valves are vital for maintaining sterile environments and accurate dosing of medications. These valves help to ensure that processes remain compliant with health regulations, ultimately safeguarding product quality. Similarly, in HVAC systems, actuator valves regulate airflow and temperature, playing an indispensable role in energy efficiency and comfort in commercial and residential buildings.
Tips: Regular maintenance of actuator valves can prolong their lifespan and ensure consistent performance in critical applications. Implementing a maintenance schedule that includes inspections and necessary adjustments can prevent unexpected failures and downtime.
Benefits of Using Actuator Valves: Efficiency and Control Advantages
Actuator valves play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and control in various industrial applications. By automating the regulation of flow, pressure, and temperature, these valves significantly reduce the need for manual intervention. According to a recent report from the International Society of Automation, implementing automated actuator valves can increase system efficiency by up to 25%, which translates into substantial cost savings for industries that rely on precise fluid management. This level of efficiency is essential in sectors such as oil and gas, chemicals, and water treatment, where operational efficiency directly impacts productivity and environmental compliance.
One of the key benefits of actuator valves is their ability to provide fine-tuned control. A study by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers highlights that facilities utilizing advanced actuator valve technology have witnessed up to a 30% improvement in process control accuracy. This enhanced precision enables businesses to optimize resource usage, minimize waste, and improve overall process reliability. Furthermore, as industries face growing pressures to adopt greener practices, the integration of actuator valves contributes to sustainability efforts by ensuring optimal resource consumption and reducing emissions through improved operational control. The ongoing advancements in actuator technology promise even greater performance enhancements, positioning them as essential components in modern automation strategies.
Understanding Actuator Valves: How They Work and Their Applications - Benefits of Using Actuator Valves: Efficiency and Control Advantages
| Dimension |
Description |
Benefits |
| Type of Actuator |
Pneumatic, Electric, Hydraulic |
Versatile operation with different energy sources |
| Control Precision |
High accuracy in flow control |
Improved process efficiency |
| Response Time |
Immediate actuation |
Faster process adjustments |
| Maintenance |
Low maintenance requirements |
Reduced downtime and costs |
| Application Areas |
Water Treatment, HVAC, Chemical Processing |
Wide applicability across various industries |