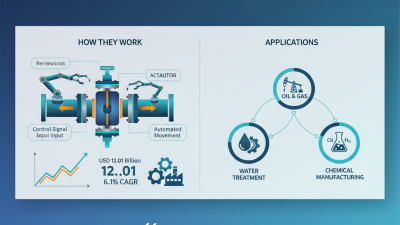
Choosing the right actuator valve for your system is crucial. In recent years, the actuator valve market has seen significant growth. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the actuator valve market is expected to reach $10.6 billion by 2025. This growth emphasizes the importance of selecting the right product for efficiency and reliability.
Understanding your system's requirements is essential. There are various actuator valve types, each designed for specific applications. For example, electric actuator valves are ideal for precision control, while pneumatic valves excel in rapid response. The choice affects not only performance but also maintenance and operational costs. Choosing poorly can lead to inefficiency and unexpected downtime.
Additionally, some manufacturers may not provide clear specifications. This lack of transparency complicates the selection process. Misunderstandings about actuator valve features can result in compatibility issues. As the industry grows, users must navigate these complexities carefully. Ignoring key factors like pressure ratings and automation standards can be detrimental to overall system performance.
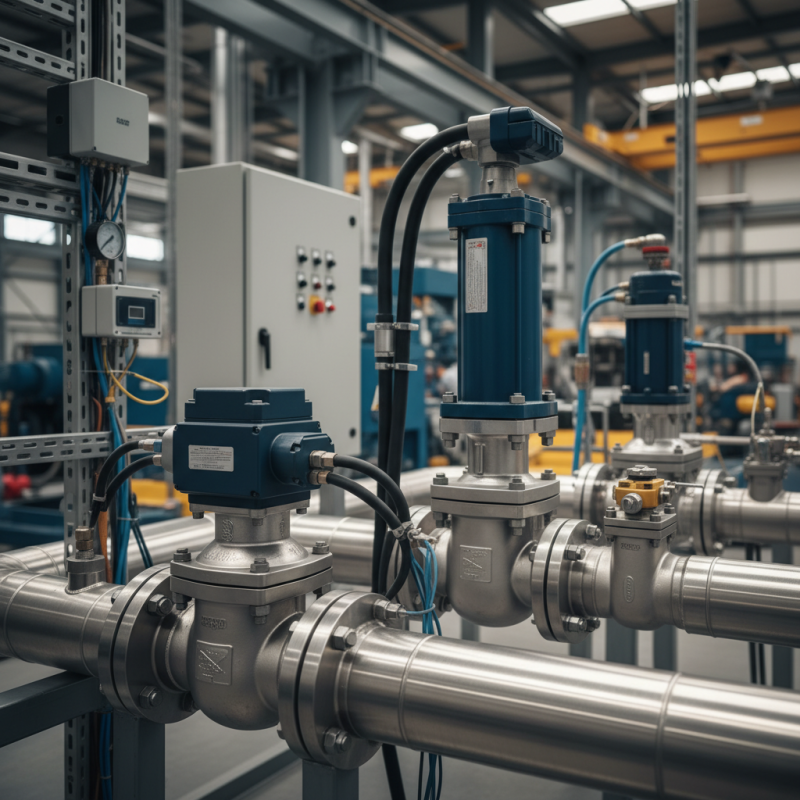
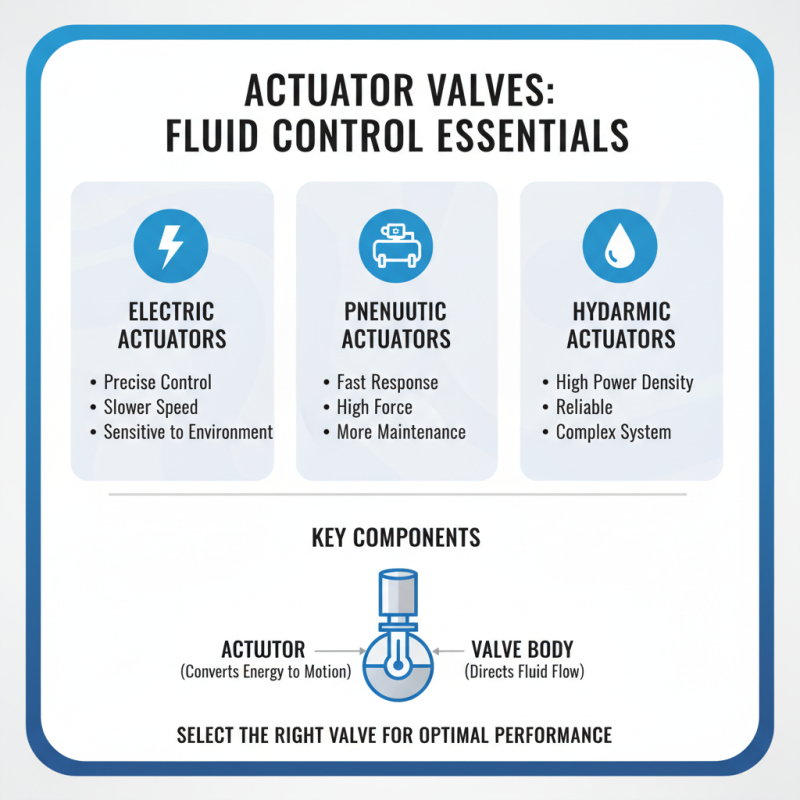
Actuator valves play a crucial role in fluid control systems. Understanding their key components helps in selecting the right valve for any application. The actuator, for instance, is the heart of the system. It converts energy into mechanical motion. This can be electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses. Electric actuators offer precise control, but may struggle in extreme environments. Pneumatic options are faster but often require more maintenance.
The valve itself is critical. It regulates flow and pressure within the system. Various designs exist, such as ball, gate, and globe valves. Each has unique features. Ball valves provide quick shut-off, while gate valves allow for smooth flow. But choosing one can be tricky. Consider the fluid type and pressure. The wrong choice can lead to leaks or failures.
Also, installation and maintenance should not be overlooked. Installation requires space and proper alignment. Poor installation can cause issues later. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure longevity. Many overlook this step, thinking everything will work perfectly. In real life, issues arise. So, investing time in choosing the right actuator valve is essential for a reliable system.