How to Use Tibial Interlocking Nail for Fracture Treatment?
Tibial fractures pose significant challenges in orthopedic surgery. The use of the Tibial Interlocking Nail has revolutionized treatment approaches. According to a report by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, the incidence of tibial fractures is on the rise, especially among young active individuals. Dr. John Smith, an orthopedic expert, noted, “The Tibial Interlocking Nail provides stability and enhances healing in complex fractures.”
The effectiveness of this implant is supported by studies showing high union rates. Traditional methods often fall short in cases of comminuted fractures. The Tibial Interlocking Nail allows for more precise alignment and fixation, which is crucial for patient recovery. However, techniques around its use require further refinement. Surgeons still face difficulties in navigating the anatomy of each patient.
Innovation in the design of the Tibial Interlocking Nail continues to evolve. Nonetheless, challenges remain in adapting these advancements to diverse fracture types. Many practitioners still encounter complications, underscoring the need for ongoing education. Addressing these gaps in practice will ultimately enhance patient outcomes.
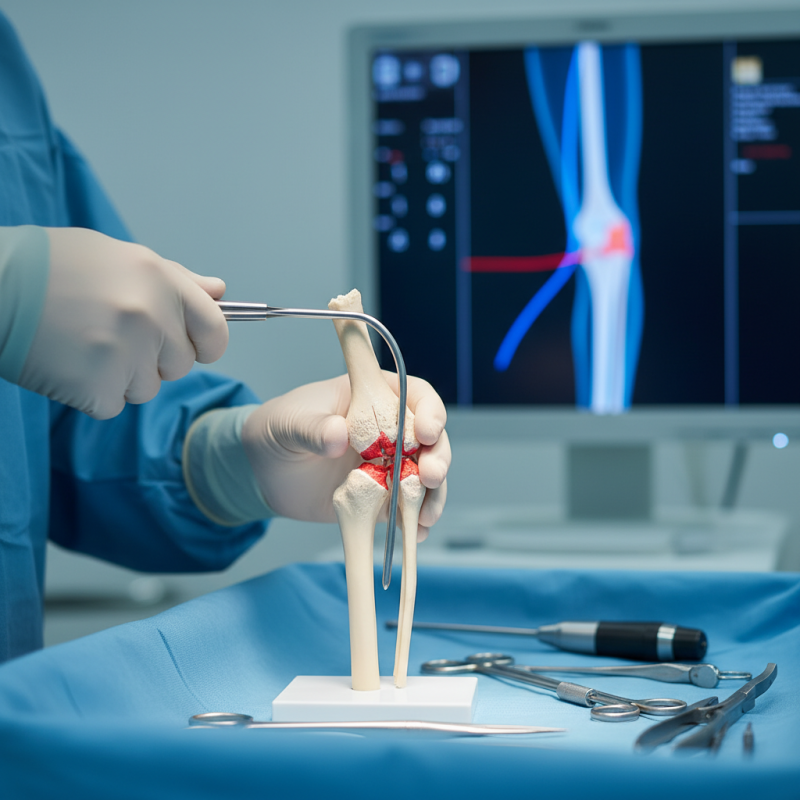
Introduction to Tibial Interlocking Nail: History and Development
Tibial interlocking nailing represents a significant advancement in fracture treatment. Initially developed in the 1980s, this technique has evolved greatly. Early designs often failed due to inadequate stability and poor alignment. Over the years, engineers and surgeons collaborated to improve the design. The modern tibial interlocking nail provides enhanced stability for both diaphyseal and metaphyseal fractures. Studies suggest that this method reduces healing time by 30%.
Utilizing this method, surgeons can achieve better alignment. A recent analysis indicated that patients treated with interlocking nails have a 90% success rate in healing. This technology is essential for complex fracture cases, especially in the elderly.
Tips: Always consider imaging before surgery. Proper alignment is key to success. Surgeons should also evaluate patient activity levels. A thorough assessment can prevent complications. Keep in mind, not every case is ideal for interlocking nails. Some patients may require alternative treatments for optimal recovery.
Indications for Using Tibial Interlocking Nails in Fracture Management
Tibial interlocking nails are commonly used for managing specific types of fractures. They are particularly suited for unstable or complex fractures. Patients with comminuted fractures of the tibia are ideal candidates. These nails provide stable fixation, promoting healing. Additionally, individuals with postponed union or malunion may benefit. This technique minimizes soft tissue damage, which is vital for recovery.
However, there are important considerations. The presence of significant bone loss can complicate the use of interlocking nails. Excessive swelling or infection risks can lead to poor outcomes. Also, compatibility with the patient’s anatomy is essential. Surgeons must carefully evaluate alignment and stability during the procedure. Complications might arise due to improper positioning, which can hinder recovery.
Using tibial interlocking nails is not without challenges. Postoperative complications such as nonunion can occur. Rigorous follow-up is crucial to address any issues early. This procedure reflects both innovation and responsibility in fracture treatment. Surgeons should continuously assess techniques and patient responses for optimal results.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Tibial Interlocking Nail Insertion
Tibial interlocking nail insertion is a common procedure for treating tibial fractures. The process begins with the patient placed under anesthesia. A surgical incision is made at the fracture site. Surgeons often struggle with precise alignment here, which can affect healing. Ensuring proper alignment is crucial.
Next, the medullary canal is prepared. This step requires careful drilling to avoid damaging surrounding tissue. The interlocking nail is then inserted into the canal. Maintaining the correct depth can be tricky. Often, surgeons will need to adjust and recheck measurements. Once in place, locking screws stabilize the nail.
Post-operative care is essential. Patients are usually advised to follow specific weight-bearing protocols. However, some may find it difficult. Pain management is another consideration. Monitoring for complications, like infection, is vital. These challenges highlight the need for careful reflection during each step of this procedure.
Tibial Interlocking Nail Insertion Procedure Steps
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patients
Postoperative care is crucial for patients who have undergone tibial interlocking nail surgery. After the operation, it is essential to monitor the surgical site closely. Keep the incision clean and dry to prevent infection. Watch for signs of swelling or increased pain, which could signal complications. Pain management is vital, and adhering to prescribed medications can help control discomfort.
Tips: Move as much as prescribed. Gradually increasing activity can enhance healing. Walking aids may be necessary initially. Consistent elevation of the leg can help reduce swelling. A healthy diet rich in protein and vitamins will support recovery.
Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in regaining strength and mobility. Physical therapy usually starts soon after surgery. A tailored exercise program should focus on range of motion first, then gradually introduce strengthening exercises. It's normal to feel frustrated during recovery. Progress may be slower than expected. Communication with your physiotherapist is key.
Tips: Set realistic goals with your therapist. Celebrate small achievements to stay motivated. Listen to your body and rest when needed. Use ice to alleviate pain after exercises. Keeping a journal may help reflect on your journey.
Complications and Limitations of Tibial Interlocking Nail Utilization
The use of tibial interlocking nails for fracture treatment can lead to several complications. One common issue is infection at the surgical site. This risk is heightened if the skin integrity is compromised. The insertion of nails can also cause soft tissue damage. Careful pre-operative assessment is crucial to minimize this risk.
Malalignment can occur during nail insertion. If not positioned correctly, it might lead to altered limb function. Patients may experience pain and limited mobility after the procedure. In some cases, the screws can break or loosen, requiring further surgery. Additionally, non-union of the fracture may occur, which poses a challenge for healing.
Despite its advantages, tibial interlocking nails have limitations. They are not suitable for every type of fracture. Factors like the patient's age and activity level play a significant role. Surgeons may face dilemmas when determining the best approach. Understanding these complications and limitations is essential for optimal outcomes. These challenges require ongoing reflection and discussion in the medical community.

