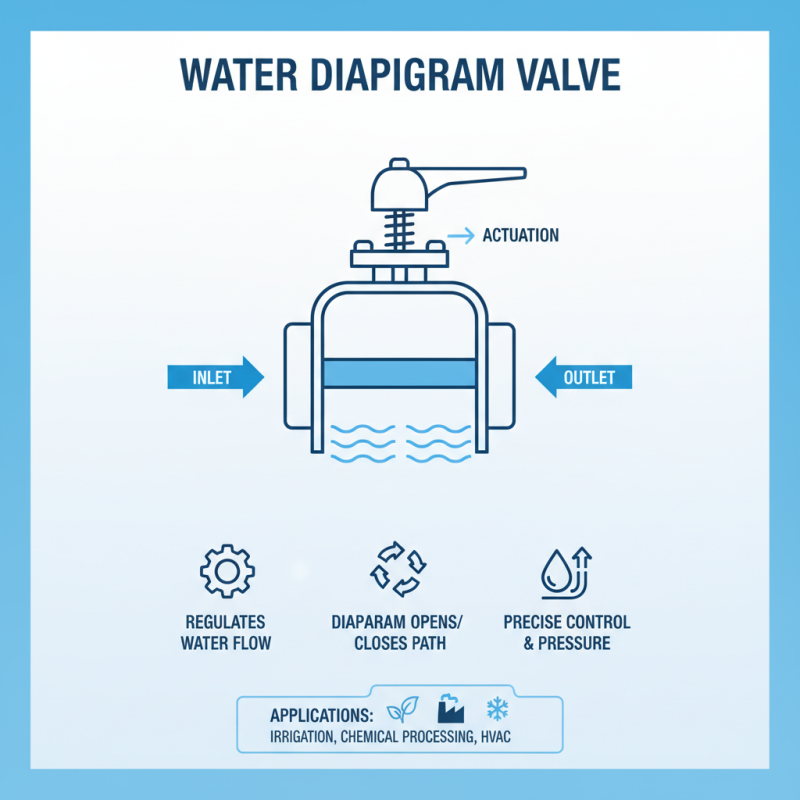
What is a Water Diaphragm Valve and How Does It Work?
Water diaphragm valves are essential components in various industries, known for their reliability and precise control in fluid management systems. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global valve market is expected to reach $102.23 billion by 2025, with diaphragm valves playing a significant role due to their advantages in handling corrosive fluids and maintaining superior sealing performance. The growing demand for efficient and reliable fluid control solutions, particularly in water treatment and chemical processing sectors, has driven attention towards the functionality and operational benefits of water diaphragm valves.
These valves utilize a flexible diaphragm to regulate flow and pressure within a system, allowing for smooth operation even under fluctuating conditions. This technology ensures minimal leakage and optimal flow regulation, making them ideal for applications where precision is critical. The increasing focus on process automation and water conservation is further intensifying the need for advanced valve solutions, highlighting the rising importance of water diaphragm valves in promoting sustainable practices and operational efficiency across multiple industries. As companies strive to enhance their fluid management strategies, understanding the workings and advantages of water diaphragm valves will be crucial for making informed decisions in system design and implementation.
What is a Water Diaphragm Valve?
A water diaphragm valve is a type of control valve that regulates the flow of water in various systems. It operates using a flexible diaphragm that separates the valve body into two chambers. When the valve is actuated, the diaphragm moves to either open or close the flow path, allowing or restricting the passage of water. This design offers precise control over flow rates and pressure, making it suitable for a range of applications such as irrigation, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
One of the key features of water diaphragm valves is their ability to provide leak-proof sealing. As the diaphragm fully closes, it creates a tight seal against the valve seat, preventing any leakage, which is essential in systems where water conservation is important. Additionally, the diaphragm's design minimizes the risk of corrosion since the internal components are not in direct contact with the flowing water. This durability makes water diaphragm valves a preferred choice for environments where reliable performance and longevity are critical.
Design and Components of Water Diaphragm Valves
Water diaphragm valves are specially designed flow control devices that utilize a flexible diaphragm to regulate the passage of fluids.
The primary components of a water diaphragm valve include the body, diaphragm, actuator, and seat. The body serves as the housing for all other components and is typically crafted from durable materials like plastic or metal to withstand various pressures and corrosion.
The diaphragm, often made of rubber or elastomer, acts like a barrier that moves up and down to either allow or restrict fluid flow through the valve.
The actuator is another crucial element that provides the necessary force to manipulate the diaphragm. It can be mechanical, pneumatic, or electrically controlled, depending on the application. When the actuator is engaged, it causes the diaphragm to flex and either close off the flow or open up the passage, effectively managing the water flow.
The seat, which provides a sealing surface for the diaphragm, ensures a tight closure, preventing leaks and ensuring that the valve operates efficiently. Together, these components work in concert to create a reliable and precise control mechanism for managing water systems in various settings, such as irrigation, industrial, and municipal applications.
How Water Diaphragm Valves Operate Mechanically
Water diaphragm valves are essential components in fluid control systems, characterized by their effective regulation of water flow. These valves operate mechanically through a simple yet robust design that utilizes a flexible diaphragm as the main sealing mechanism. When the valve is actuated, the diaphragm is pushed or pulled, either closing off the flow completely by sealing against the valve seat or opening to allow water to pass through.
The operation of a diaphragm valve involves several key components: the body, the diaphragm, and the actuator. When pressure is applied, the actuator moves the diaphragm, enabling a precise control of flow rates. This movement can be manual or automated, depending on the specific application. The diaphragm's flexibility allows it to adapt easily to pressure changes, making the valve reliable in various operating conditions. Additionally, the construction of diaphragm valves often incorporates materials resistant to corrosion and wear, further enhancing their longevity and performance in water management systems.
What is a Water Diaphragm Valve and How Does It Work?
| Feature |
Description |
| Function |
Controls the flow of water in a pipeline by using a flexible diaphragm. |
| Mechanism |
Operates mechanically through the flexing of the diaphragm in response to pressure changes. |
| Materials |
Typically made from elastomers like rubber or plastic for flexibility and durability. |
| Applications |
Used in various industries, including water treatment, agriculture, and plumbing systems. |
| Advantages |
Offer precise flow control, low maintenance requirements, and can handle different fluid types. |
| Disadvantages |
May have limitations in high-pressure applications compared to other valve types. |
| Maintenance |
Regular checks for wear and tear of the diaphragm are recommended. |
Applications of Water Diaphragm Valves in Various Industries
Water diaphragm valves are essential components used across various industries for fluid control. Their primary application lies in regulating the flow of water and other fluids, which is crucial in sectors such as agriculture, water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and HVAC systems. According to a recent industry report, the global water diaphragm valve market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2023 to 2028, driven by increasing investments in water infrastructure and wastewater management.
In agriculture, water diaphragm valves facilitate efficient irrigation systems, allowing farmers to optimize water usage and improve crop yield. The ability to control water flow accurately leads to more sustainable farming practices, which is critical as global water scarcity continues to rise. In the water treatment industry, these valves are integral for processes like filtration and chemical dosing, ensuring that the water meets safety standards. The pharmaceutical sector also relies on diaphragm valves for sterile applications, where precise fluid control is necessary to maintain cleanliness and avoid contamination.
Tips for selecting the right diaphragm valve include considering the fluid type, pressure requirements, and compatibility with existing systems. Additionally, regular maintenance can enhance the longevity and reliability of these valves, making it essential for industries to implement comprehensive inspection routines. Understanding these factors can significantly impact operational efficiency and safety.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Water Diaphragm Valves
Water diaphragm valves offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for controlling fluid flow in various applications. One significant benefit is their ability to provide precise flow control, thanks to the flexible diaphragm that directly interacts with the fluid. This allows for smooth regulation and minimal turbulence, which is particularly important in systems requiring accurate flow management. Additionally, diaphragm valves are typically resistant to corrosion and wear, especially when constructed from suitable materials, making them ideal for use in different water treatment processes and chemical handling.
However, there are limitations to consider when using water diaphragm valves. One notable drawback is their sensitivity to pressure fluctuations; excessive pressure can lead to diaphragm damage or valve failure. Moreover, these valves may not perform as efficiently in high-pressure applications due to potential limitations in seating pressure and sealing capabilities. Maintenance is another factor to weigh, as the diaphragm may require periodic replacement, leading to increased operational costs and potential downtime. Balancing these advantages and limitations is crucial for determining the suitability of water diaphragm valves in specific applications.